I. Introduction
Artificial intelligence (AI) alters how we conduct business and live our lives. The use of AI in our daily lives is increasing. Especially with the launch of OpenAI GPT and Google Bard, the world is curious about their futures. and how this invention will affect their businesses and lives. As we are moving forward, web 2.0 vs web 3.0 is becoming a topic of debate around the world. The evolution of the internet has led to the development of three distinct phases, Web 1.0, Web 2.0, and Web 3.0. Each phase represents a significant advancement in technology, design, and user experience. In this article, we will compare Web 1.0 vs Web 2.0 vs Web 3.0 for advantages, disadvantages, and characteristics.
A. Definition of Web 1.0
Web 1.0, or the “static web,” was the initial iteration of the World Wide Web. That refers to the early days of the internet when most websites only allowed for one-way transmission of information. The information was presented in a straightforward format with no dynamic elements. Aside from reading content, users couldn’t do anything else on the helpful site.
B. Definition of Web 2.0
The term “Web 2.0,” which can also be shortened to “Social Web,” describes the current iteration of the internet. The paradigm shifted dramatically in favor of user-generated content and interactive dialogue. During this period, the internet saw the rise of new types of websites, such as social networking sites, blogs, and wikis. Websites became more interactive and aesthetically pleasing to boost visitor retention and return visits.
C. Definition of Web 3.0
The current stage of the internet’s evolution is known as Web 3.0 or the semantic web. One thing that makes it what it is is how content gets more complex and personalized. We are moving toward a more data-driven and connected internet, where context and analytics are essential for making predictions. Web 3.0’s main objective is to provide users with a unique and straightforward journey.

II. Comparison of Web 1.0, Web 2.0, and Web 3.0
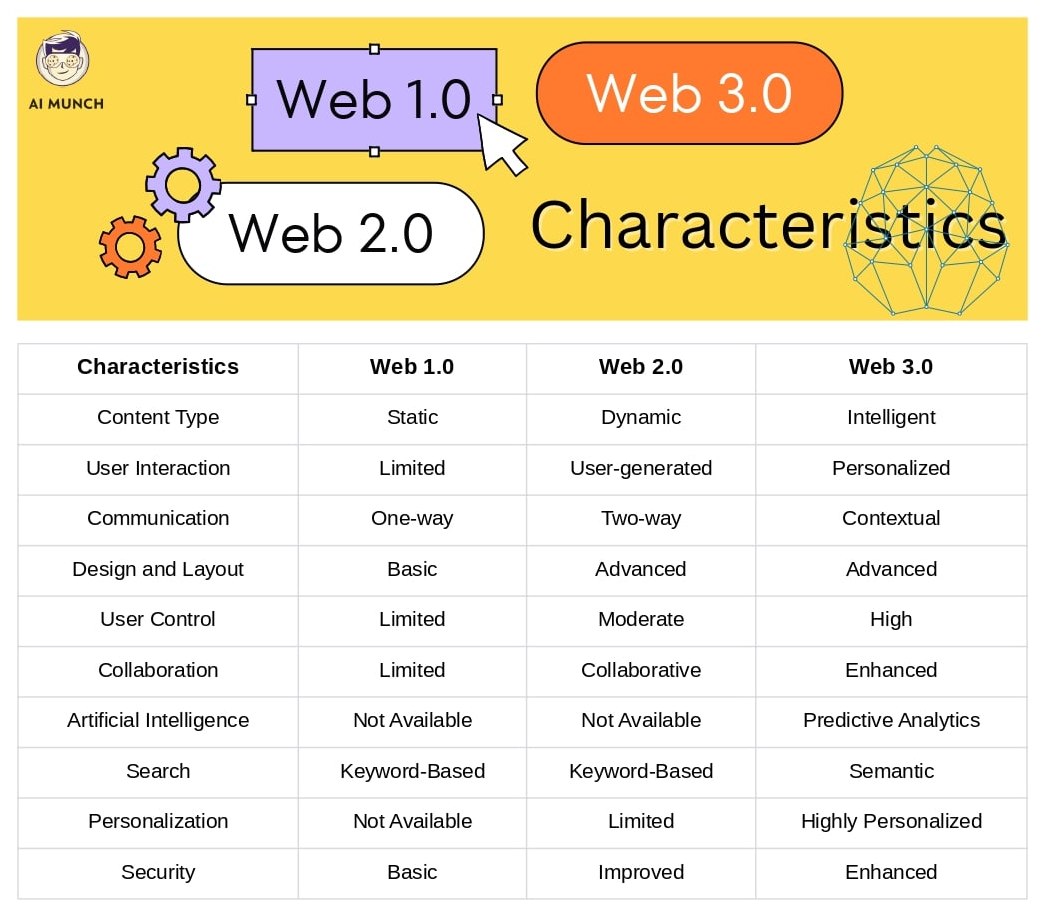
A. Characteristics of Web 1.0
- Static content – Web 1.0 websites were primarily designed for one-way communication. The content was static and delivered in a basic design and layout.
- Limited user interaction – Users could consume information but had limited interaction with the website. The websites were designed to deliver information rather than facilitate engagement.
- One-way communication – Websites were designed for one-way communication, and users had limited opportunities to interact with the website.
- Basic design and layout – Web 1.0 websites had a basic design and layout. The emphasis was on delivering information rather than creating an engaging user experience.
B. Characteristics of Web 2.0
- Dynamic content – Web 2.0 websites became more dynamic, with an emphasis on user-generated content. Users could create and share content, and websites became more visually appealing.
- User-generated content – User-generated content became a significant part of Web 2.0. Social networking sites, blogs, and wikis emerged as platforms for users to create and share content.
- Two-way communication – Web 2.0 websites were designed for two-way communication, with an emphasis on engaging the user. Websites became more interactive, and users had more opportunities to interact with the website.
- Advanced design and layout – Web 2.0 websites had more advanced design and layout. The emphasis was on creating an engaging and intuitive user experience.
C. Characteristics of Web 3.0
- Intelligent content – Web 3.0 is focused on delivering intelligent and personalized content. Websites are becoming more data-driven, with an emphasis on context and predictive analytics.
- Contextual content – Web 3.0 is focused on delivering contextual content that is relevant to the user’s needs and preferences. Websites are becoming more personalized and intuitive.
- Predictive analytics – Web 3.0 is becoming more data-driven, with an emphasis on predictive analytics. Websites can predict what the user is looking for based on their behavior and preferences.
- Personalization – Web 3.0 is focused on delivering a personalized and intuitive user experience. Websites can deliver content that is relevant to the user
III. Examples of Web 1.0, Web 2.0, and Web 3.0
A. To illustrate Web 1.0, here are some examples: When “Web 1.0” was first used, it referred to when most websites were static and worked like online brochures. Web 1.0 sites include Yahoo! and AltaVista, the first version of Amazon, and simple online directories like the virtual analogs of the paper Yellow Pages.
B. To illustrate Web 2.0, consider the following: Web 2.0 sites constantly change and allow users to contribute to the content, work together, and share knowledge. Social networking sites like Facebook and Twitter, platforms for user-generated content like YouTube and Wikipedia, and collaborative knowledge-sharing sites like Quora and Stack Overflow are all examples of Web 2.0 sites.
C. Instances of Web 3.0, It’s the early days of Web 3.0: However, some examples of Web 3.0 technologies and applications include intelligent virtual assistants like Amazon’s Alexa, Google assistant, and Apple’s Siri, semantic web technologies that help computers understand the meaning of data on the internet, and personalized search engines like Google Now.
IV. Advantages and Disadvantages of Web 1.0, Web 2.0, and Web 3.0
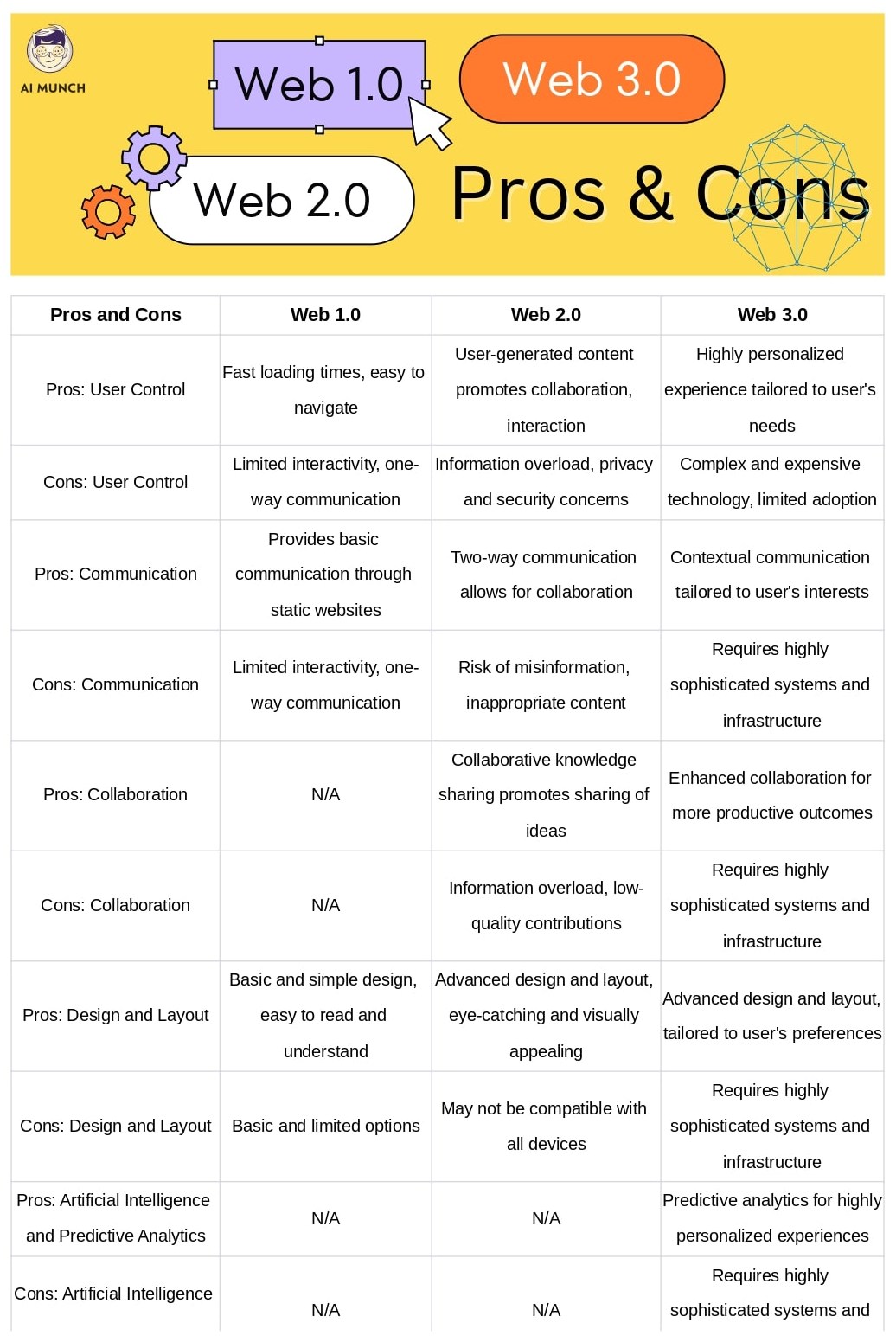
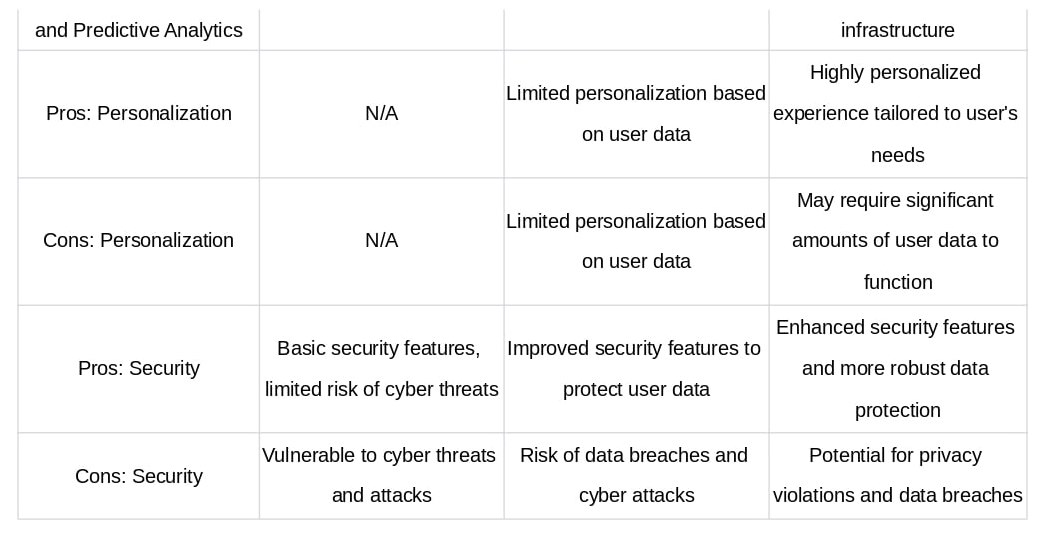
A. Advantages of Web 1.0
Simplicity and ease of use: Web 1.0 sites were simple and easy to navigate, with a limited number of pages and straightforward designs.
Fast loading times: Because Web 1.0 sites were mainly static, they loaded quickly even with slow internet connections.
Basic design and layout: The basic design and layout of Web 1.0 sites made them easy to use and access.
B. Disadvantages of Web 1.0
Limited interactivity: Web 1.0 sites were mainly one-way communication channels, with limited interactivity and user engagement.
One-way communication: Web 1.0 sites were mostly static and provided information to users, without giving them the ability to interact with the content or contribute to it.
Lack of personalization: Web 1.0 sites were not personalized to individual users, which made it difficult to provide them with targeted content and recommendations.
C. Advantages of Web 2.0
User-generated content: Web 2.0 sites allow users to generate and share content, which leads to a more diverse and comprehensive range of information.
Collaborative knowledge sharing: Web 2.0 sites promote collaboration and knowledge sharing among users, which can lead to the creation of new ideas and insights.
Two-way communication: Web 2.0 sites allow for two-way communication between users and content creators, which can lead to more engagement and interaction.
D. Disadvantages of Web 2.0
Information overload: With the abundance of user-generated content on Web 2.0 sites, it can be difficult to filter out the noise and find accurate and reliable information.
Privacy and security concerns: Web 2.0 sites collect a lot of user data, which can raise privacy and security concerns for users.
Risk of misinformation: Because anyone can create and share content on Web 2.0 sites, there is a risk of spreading misinformation and false information.
E. Advantages of Web 3.0
Personalized user experience: Web 3.0 technologies allow for personalized user experiences, which can lead to more engagement and satisfaction.
Intelligent and contextual content: Web 3.0 technologies can help computers understand the context of information, which can lead to more relevant and helpful
F. Disadvantages of Web 3.0
Complex and expensive technology: The high-priced complexity of the technology required to fully realize Web 3.0 is undoubtedly one of its most significant drawbacks. AI, blockchain, and the Internet of Things (IoT) are just a few cutting-edge technologies that power Web 3.0. (IoT). These methods are still in their early stages and will take a lot of time and money to develop and use correctly. Startups and small businesses may find this hard to do because they need more money or knowledge to implement these technologies.
Limited adoption and availability: The fact that Web 3.0 is not widely used and available is a significant drawback. Although the concept of Web 3.0 has been around for a while, its implementation and widespread use are still in their infancy. This means that the idea and its benefits still need to be discovered to the general public. Furthermore, only some places worldwide have the infrastructure required to support Web 3.0. For example, some areas need more infrastructure to support Web 3.0 applications, like high-speed internet connections or up-to-date computers and software.
V. Conclusion
Of Course, AI is affecting us in many ways, Web is one of those. Web 1.0 had a simple layout, one-way communication, and content that didn’t change. With Web 2.0, things like user-generated content, two-way communication, and advanced design and layout were made possible. Web 3.0 is characterized by content that is smart and relevant to the user, a personalized user experience, and cutting-edge predictive analytics. In Web 1.0 vs Web 2.0 vs Web 3.0, Web3 is the clear winner.
Future implications of Web 3.0 for businesses and consumers
As the web continues to change, businesses and consumers must get used to the new rules set by Web 3.0. Because of how intelligent and flexible the web is, it will be easier for companies to offer personalized support to their customers, making them happier and more loyal. In addition, with the help of predictive analytics, companies can provide products and services to customers before they are even asked for.
From the user’s point of view, the intelligent web will make online experiences faster and more personalized. Virtual assistants (such as Siri, and Alexa) and other forms of artificial intelligence will make it easier and quicker for people to use websites by giving them more relevant information.
Importance of staying up-to-date with technological advancements
Both companies and individuals benefit greatly from keeping abreast of technological developments. Keeping up with the times can prevent you from missing out on opportunities and being left behind in today’s competitive business environment. People and businesses can stay competitive and ahead of the curve if they keep learning about and using the latest technological advances.
In sum, Web 1.0, Web 2.0, and Web 3.0 are distinct phases in developing the internet, each with its own features and benefits. To take advantage of what the intelligent web offers and stay ahead of the curve in the years to come, businesses and people need to keep up with the latest technology.
FAQs
We are currently in the era of Web 3.0, also known as the Semantic Web or the Intelligent Web.
Google is not considered a Web3 platform, but it is actively working on integrating some of the technologies and principles of Web3, such as blockchain and decentralized systems, into its operations.
Characteristics and capacities are where Web 1.0, Web 2.0, and Web 3.0 diverge most clearly from one another. Web 1.0’s characteristics are its static nature, lack of user participation, unidirectional communication, and simplistic layout and design. Characteristics of Web 2.0 include user-generated content, two-way communication, sophisticated design and layout, and dynamic content. Intelligent content, contextual content, predictive analytics, and personalization are hallmarks of Web 3.0.
Blockchain-based platforms like Ethereum, which make building and running decentralized applications (dApps) possible, are a common example of Web 3.0.
A real-life example of Web3 is using smart contracts in the real estate industry. Smart contracts use blockchain technology to automatically negotiate and carry out the terms of an agreement between two parties. These contracts are self-executing.
A single individual or organization did not start Web3 but rather emerged as a community-driven effort to create a more decentralized and democratic web.
The concept of Web 4.0 remains unrealized at this point. Virtual and augmented reality, cutting-edge artificial intelligence, and brain-computer interfaces are all technologies and capabilities that have been bandied about as part of Web 4.0.
Do you want to read more? Check out these articles.










Hello! If you’re in need of data scraping services, I’d be
happy to assist you. As an expert in this field, I
have the experience and tools necessary to provide fast and accurate
data scraping that can help you make informed decisions and
grow your business. Don’t hesitate to reach out to me for any
of your data scraping needs. Rosaria